Be a beekeeper
Published 12:00 am Sunday, January 24, 2021
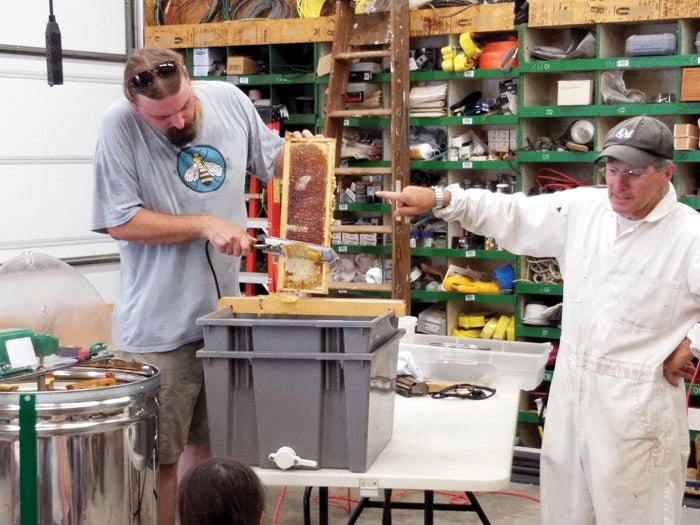

- Bryan Fisher and Marcel Renn are two Master Beekeepers who will be teaching the Beginning Beekeeper School
By Amy-Lynn Albertson
Rowan County Extension
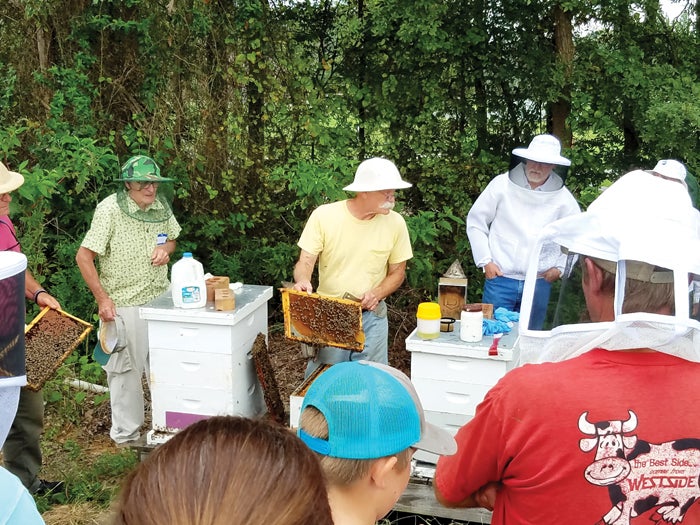
The Rowan County Beekeepers Association is offering a virtual Beginning Beekeeping school in four Saturday morning classes — Feb. 27, March 6, March 13, and March 20 from 8 a.m.-noon. The course cost is $50, including 16 hours of training with Journeyman and Master Beekeeper speakers, Beginning Beekeeper book, resource notebook, resource handouts, presentations, and a one-year membership to Rowan County Beekeepers Association. Journeyman and Master Beekeepers will teach the class over Zoom, and the sessions will be recorded so participants will be able to watch them again after class. To register for the course, go to go.ncsu.edu/2021beekeepingschool. Learn the basics of being a beekeeper and managing your bees.
Honeybees account for an estimated $70 million of North Carolina’s agriculture industry between pollination and honey. North Carolina beekeepers also produce a wide variety of bee products from the beehive with their honey bees’ aid. The products have various uses such as beeswax for candles, cosmetics, royal jelly for cosmetics, bee pollen as a protein source, and more. These products, though popular, are not the primary importance of honey bees in the state. Honey bees are the most important pollinators of food crops for humans and probably food for wildlife in North Carolina and the entire nation. You might ask, “Don’t other insects pollinate as well?” The answer is yes, but none with the unique features that honey bees possess. A honey bee colony may consist of up to 60,000 individuals, while most other insects are solitary or only have colonies of a few hundred individuals. Beekeepers can move honey bee colonies to any location where bees are needed for pollination, which is not usually an option with other insects. Honey bees are also important in pollinating many fruits, vegetables, and seeds in the home garden. Honeybees use nectar to make honey. Nectar is almost 80% water with some complex sugars. They use their long, tubelike tongues like straws to suck the nectar out of the flowers, and they store it in their “honey stomachs.” Bees have two stomachs, their honey stomach, which they use like a nectar backpack, and their regular stomach. The honey stomach holds almost 70 mg of nectar, and when full, it weighs almost as much as the bee does. Honeybees must visit between 100 and 1,500 flowers to fill their honey stomachs.
The honeybees return to the hive and pass the nectar onto other worker bees. These bees suck the nectar from the honeybee’s stomach through their mouths. These “house bees” “chew” the nectar for about half an hour. During this time, enzymes break complex sugars in the nectar into simple sugars so that it is both more digestible for the bees and less likely to be attacked by bacteria while it is stored within the hive. The bees then spread the nectar throughout the honeycombs, where water evaporates from it, making it a thicker syrup. The bees make the nectar dry even faster by fanning it with their wings. Once the honey is gooey enough, the bees seal off the honeycomb cell with a plug of wax. The honey is stored until it is eaten. In one year, a colony of bees eats between 120 and 200 pounds of honey. Bees use the stored honey for food during the winter months. The honey that you see at the farmers’ market and in the grocery store is usually harvested in the summer months when there are many blooming plants with nectar.
Bees are wonderful, fascinating, essential creatures vital to our health and the health of our planet. They are primary pollinators for flowers, gardens and crops and are responsible for pollinating at least a third of the foods we eat. Beekeeping is a very fulfilling hobby and can be financially beneficial when your hives produce extra honey and beeswax to sell or gift to others. Beekeeping can be a lifelong learning experience. Bees have a complex society that is endlessly fascinating to observe and learn about. Beekeeping is also a social experience where experienced beekeepers can mentor and talk to you, attend association meetings and conferences, and talk to family and friends about your bees.
For more information about honeybees or the Rowan County Beginning Beekeeper School, contact Rowan County Cooperative Extension at 704-216-8970 or go to rowan.ces.ncsu.edu.
Amy-Lynn Albertson is director of the Rowan County Extension.